From: Wang, Y. and Bourouiba, L. (2021) Growth and breakup of ligaments in unsteady fragmentation. Journal of Fluid Mechanics. 910:A39.
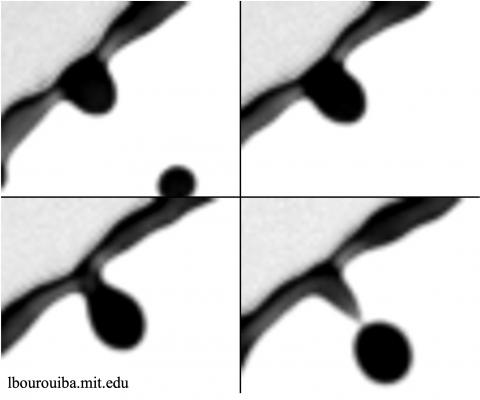
Abstract: We elucidate the physics underlying the birth, evolution and breakup of ligaments on a rim bounding an unsteady liquid sheet. This rim destabilizes into corrugations that can grow into ligaments, which in turn, break into secondary droplets via end-pinching. Combining experiments and theory, we show that not all corrugations can grow into ligaments. The number of corrugations is captured by linear instability coupled with nonlinear rim thickness self-adjustment and scales as Nc∼We3/4 with Weber number, We. The number of ligaments scales as Nℓ∼We3/8. The growth of a ligament is governed by the competition between the constraint imposed by the geometry of the local rim–ligament junction; the local force balance including the fictitious force from the continuously decelerating rim; and the global rim mass conservation constraint. The temporal evolution of the average width of ligaments is predicted. Key to understanding the ligament population, a minimum distance between two corrugations is required to enable their actual transition into ligaments. By predicting this minimal distance, we derive the evolution of the number of ligaments. We show that droplets are shed, one at a time, following a chaotic dripping end-pinching regime independent of We. Finally, the number of droplets shed per unit of time decreases over time and scales as Sd∼We3/4; while the volume shed per unit of time increases over time and is independent of We. Theoretical predictions are validated without fitting parameters.