Fluid Dynamics and Disease Projects
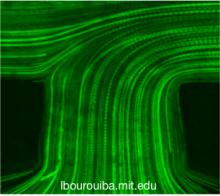 |
Fluid flow measurements and quantification at the microscale matters for health: How flow-cell interactions help understand obstruction of key medical devices and suggest novel designs |
The treatment of hydrocephalus often involves the placement of a shunt catheter into the cerebrospinal ventricular space, though such ventricular catheters often fail by tissue obstruction. While diverse cell types contribute ... more |
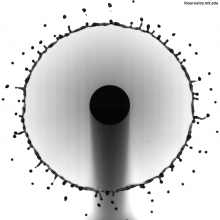 |
Universal Rim Thickness in Unsteady Sheet Fragmentation: Unsteady breakup of Newtonian to biological viscoelastic complex fluids |
Unsteady fragmentation of a fluid bulk into droplets is important for epidemiology as it governs the transport of pathogens from sneezes and coughs, or from contaminated crops in agriculture. It is also ubiquitous in industrial processes such as paint, coating, and combustion. Unsteady fragmentation is distinct from steady fragmentation on which most theoretical efforts have been focused... more |
 |
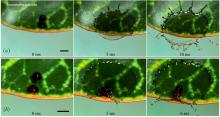
Water-to-air transfer: Bubbles at the interface |
Bubbles are ubiquitous in industrial and environmental processes, indoors and outdoors, and have an important impact on a wide range of systems. They can be beneficial in mixing bulk water, they contribute significantly to the planetary-scale transfer of chemical and organic compounds from water bodies to the atmosphere and they are also a source of illness and contamination. Upon reaching the air–water interface, bubbles can be the source of hundreds of droplets transporting the organisms, chemicals or particles from the bulk in which they traveled to the air that we breathe. An... more |
 |
Unsteady sheet fragmentation: from compliance, wetting, non-isolated drop impacts, to secondary drops and contamination |
Understanding what shapes the drop size distributions produced from fluid fragmentation is important for a range of industrial, natural and health processes. Fluid fragmentation plays an important role in pathogen transmission in particular. A particular example is from impacts on contaminated surfaces already, some dry, and others already wet, supporting sessile drops. These are ubiquitous in the field, where plant pathogens are attached to leaves via sticky mucilage requiring dissolution (e.g., spores of rust). The Crescent-moon fragmentation is one of the most efficient... more |
 |
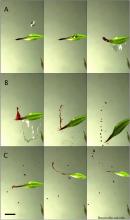
Fluid fragmentation shapes rain-induced foliar disease transmission |
Plant diseases represent a growing threat to the global food supply. The factors contributing to pathogen transmission from plant to plant remain poorly understood. Statistical correlations between rainfalls and plant disease outbreaks were reported; however, the detailed mechanisms linking the two were relegated to a black box. In this combined experimental and theoretical study, we focus on the impact dynamics of raindrops on infected leaves, one drop at a time. We find that the deposition range of most of the pathogen-bearing droplets is constrained by a hydrodynamical condition and we... more |
 |
Rain-induced foliar pathogen ejection |
Plant diseases are a major cause of losses of crops worldwide. Although rainfalls and foliar disease outbreaks are correlated, the detailed mechanism explaining their link remains poorly understood. The common assumption from phytopathology for such link is that a splash is generated upon impact of raindrops on contaminated liquid films coating sick leaves. We examine this assumption using direct high-speed visualizations of the interactions of raindrops and leaves over a range of plants. We show that films are seldom found on the surface of common leaves. We quantify the leaf- surface’s... more |
 |
Surface-tension phenomena in organismal biology: human |
Flows driven by surface tension are both ubiquitous and diverse, involving the drinking of birds and bees, the flow of xylem in plants, the impact of raindrops on animals, respiration in humans, and the transmission of diseases in plants and animals, including humans. The fundamental physical principles underlying such flows provide a unifying framework to interpret the adaptations of the microorganisms, animals, and plants that rely upon them. The symposium on ‘‘Surface-Tension Phenomena in Organismal Biology’’ assembled an interdisciplinary group of researchers to address a large... more |
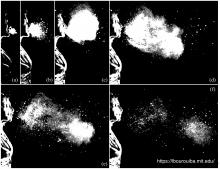 |
Violent Expirations: importance of the turbulent multiphase flow |
Violent respiratory events such as coughs and sneezes play a key role in transferring respiratory diseases between infectious and susceptible individuals. We present the results of a combined experimental and theoretical investigation of the fluid dynamics of such violent expiratory events. Direct observation of sneezing and coughing events reveals that such flows are multiphase turbulent buoyant clouds with suspended droplets of various sizes. Our observations guide the development of an accompanying theoretical model of pathogen-bearing droplets interacting with a turbulent buoyant... more |
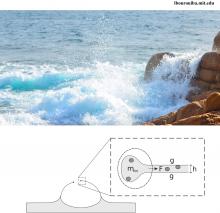 |
Interactions between bubbles and microorganisms |
Bubbles are ubiquitous in biological environments, emerging during the complex dynamics of waves breaking in the open oceans or being intentionally formed in bioreactors. From formation, through motion, until death, bubbles play a critical role in the oxygenation and mixing of natural and artificial ecosystems. However, their life is also greatly influenced by the environments in which they emerge. This interaction between bubbles and microorganisms is a subtle affair in which surface tension plays a critical role. Indeed, it shapes the role of bubbles in mixing or oxygenating... more |
 |
Fluid fragmentation from hospital toilets |
Hospital-acquired infections represent significant health and financial burdens to society. Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) is a particularly challenging bacteria with the potential to cause severe diarrhea and death. One mode of transmission for C. difficile, as well as other pathogens, which has received little attention is the potential air contamination by pathogen-bearing droplets emanating from toilets. In the fluid dynamics video submitted to the APS DFD Gallery of Fluid Motion 2013, we present flow visualizations via high-speed recordings showing the capture of the product of... more |
 |
Surface-tension phenomena in organismal biology: plants |
Flows driven by surface tension are both ubiquitous and diverse, involving the drinking of birds and bees, the flow of xylem in plants, the impact of raindrops on animals, respiration in humans, and the transmission of diseases in plants and animals, including humans. The fundamental physical principles underlying such flows provide a unifying framework to interpret the adaptations of the microorganisms, animals, and plants that rely upon them. The symposium on ‘‘Surface-Tension Phenomena in Organismal Biology’’ assembled an interdisciplinary group of researchers to address a large... more |
 |
Drops and bubbles in the environment |
Bubbles and drops are ubiquitous in nature and play critical roles in many important environmental processes. Most familiar is the life-sustaining role of rain. Less familiar are their roles in the thermal budget of the atmosphere and their role in pathogen dispersal. In this paper, we highlight new applications where drops and bubbles have important impacts on the environment and health arenas. The paper highlights the physical processes that enable the creation of drops and bubbles and the new challenges that they raise. Among them, we discuss, in particular, the role of drops and... more |
